Help me understand how the “Tone” control works. What does it actually do?
What adjustments on an active bass mirror the same effect?
From what I can tell looking inside - it connects to a potentiometer that has a diode or other component bypassing the pot. I’m presuming that is some sort of filter that allows select frequencies through, and then the tone control is effectively a volume nob turning down all the other frequencies.
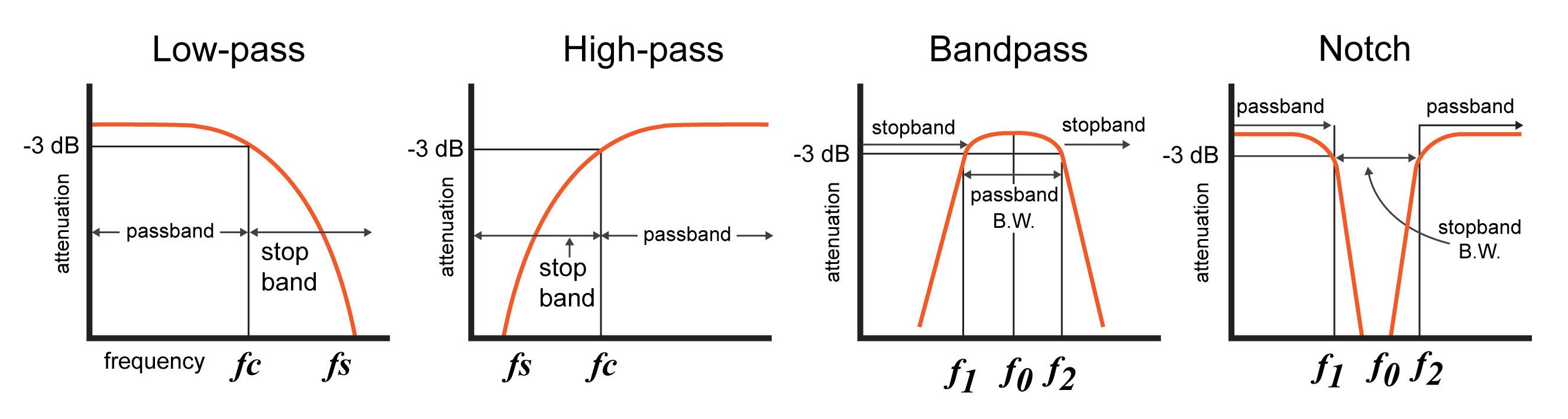
Is that a low pass filter? Everything below a threshold?
A band pass filter? Everything within a range?
What frequencies are these filters typically at?
Taking that concept, what adjustments on an active eq bass achieve the same effect? Just turning down the highs?
I’m also figuring out how to use this to greater effect with a passive bass and another EQ in the chain. Like - use the EQ to boost the mids above the normal Tone cutoff range, and then use the nob as a quick control of how prominent those are.
4 Likes
Tone control is essentially a low pass filter, filtering out the higher treble frequencies. With varying degrees of success.
2 Likes
The Tone Control is a low pass filter. Meaning, it allows the low to pass while rolling off the highs.
Exactly what the Tone Control does is variable, encompassing the pickups, resistor used (like an orange drop), and the potentiometer.
Take a look at this…
(2) How Tone controls work | TalkBass.com https://share.google/PxEEmeO9WxtdPsib8
3 Likes
Woah. Those curves are weird.
That does give a clearer understanding of what it’s doing.
That feels very different from what I’d expect to get from an active preamp.
1 Like
I’m recently a filter geek, started getting in to them last year studying some DSP programming - interesting stuff but it gets deep pretty fast, but I can explain some of this.
A tone control, like the others mention, is a low pass filter. The circuit used in nearly every bass is in fact a first-order RC filter. First order filters will attenuate signals past their cutoff frequency with a slope of -6dB/octave. The cutoff frequency in a RC filter is a function of both the resistance and the capacitance, so the tone pot adjusts the cutoff frequency.
An active bass usually has a 2 or 3-band EQ. An Equalizer circuit is (usually) a set of second order (or higher) hi/lo shelving or peaking bandpass filters, depending on the EQ. These are active filter circuits very different from the simple RC filter in a passive tone control, and are usually based on opamps with feedback and resistors/capacitors affecting that.
Many primers online, here’s an example:
https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/technical-articles/an-introduction-to-filters/
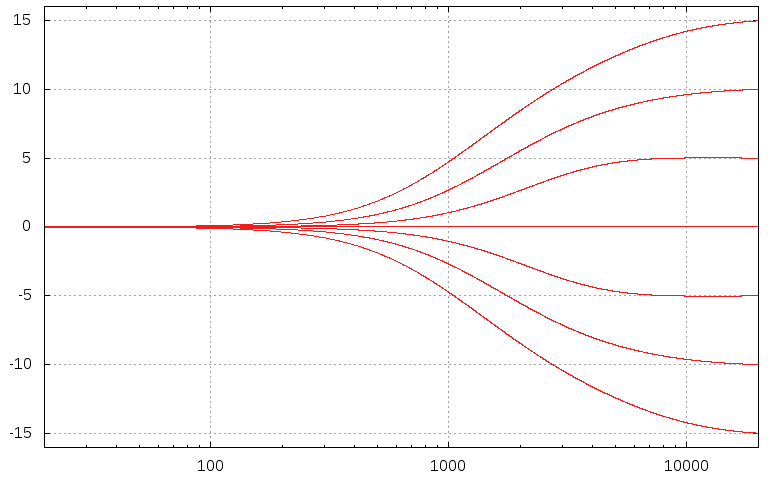
High shelf filter example (at various values for boost or cut):
Another article showing the diff between peaking and bandpass:
7 Likes